ROKO
List (리스트) 본문
728x90
Linear list
선형적인 순서를 가진 항목들의 집합
Commonalities
- Linear data structure
Differences
- List can add and delete item at any index
ArrayList

Implemenatation
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//Remember : array index starts at 0 !
class ArrayList{
const static int MAX_SIZE = 100;
int data[MAX_SIZE];
int length;
public:
ArrayList(){length = 0;}
void insert(int pos,int item){
if(full()) throw 'list is full';
if(pos<0 || pos>length) throw 'out of index';
for(int i=length; i>pos; i--){
data[i]=data[i-1];
}
data[pos] = item;
length++;
}
void remove(int pos){
if(empty()) throw 'list is empty';
if(pos<0 || pos>=length) throw 'out of index';
for(int i=pos+i; i<length; i++){
data[i-1] = data[i];
}
length--;
}
int get(int pos){return data[pos];}
bool empty(){return length == 0;}
bool full(){return length == MAX_SIZE;}
int size(){return length;}
int find(int item){
for(int i=0; i<length; i++){
if(data[i] == item) return i;
}
throw 'cannot find the item';
}
void replace(int pos, int item){
if(pos<0 || pos>length) throw 'out of index';
data[pos] = item;
}
void display(){
for(int i=0; i<length; i++){
cout<< data[i] << " ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
void clear(){length = 0;}
};Time complexity
- insert(pos, item) : O(n)
- remove(pos) : O(n)
- find(item) : O(n)
- get/replace : O(1)
Space
- n : for n data
Pros & Cons
pros
- 차지하는 공간이 link사용보다 적음
- random access 가능
cons
- 가변 데이터 크기를 다룰 수 없다.
ArrayList는 가변적인 데이터 크기를 다루지 못해 단점이 있다. 이를 해결하기 위해서 LinkedList를 사용할 수 있는데,
LinkedList 는 link(prev, next) 개수와 구현방식에 따라 CircularLinkedList, SinglyLinkedList, CircularLinkedList, Double LinkedList로 나뉜다.
SinglyLinkedList

Implementation
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node{
private:
int data;
Node* link;
public:
Node(int val=0) : data(val),link(nullptr){}
Node* get_link(){return this->link;}
void set_link(Node* next) {this->link = next;}
bool hasData(int val){return this->data == val;}
void setData(int data){this->data = data;}
int getData(){return this->data;}
};
class SinglyLinkedList{
private:
Node head;
int cnt;
Node* getHead(){return head.get_link();}
Node* getNode(int pos){
Node* p = &head;
for(int i=-1; i<pos; i++){
//check head node
if(p == nullptr) break;
p = p->get_link();
}
return p;
}
public:
SinglyLinkedList(){
this->cnt = 0;
}
bool empty(){
return this->getHead() == nullptr;
}
int size() {return this->cnt;}
void display(){
cout<<"Size: "<<this->size()<<endl;
for(Node* p=getHead(); p!=nullptr; p=p->get_link()){
cout<<p->getData()<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
void insert(int pos, int data){
if(!(pos>=0&&pos<=size())) throw 'out of range';
Node* prev = this->getNode(pos-1);
if(prev!=nullptr){
Node* p = new Node(data);
p->set_link(prev->get_link());
prev->set_link(p);
this->cnt++;
}
}
void remove(int pos){
if(!(pos>=0&&pos<=size())) throw 'out of range';
Node* prev = this->getNode(pos-1);
if(prev != nullptr){
Node* removed = prev->get_link();
prev->set_link(removed->get_link());
delete removed;
this->cnt--;
}
}
int find(int query){
int idx = 0;
for(Node* p=getHead(); p!=nullptr; p=p->get_link()){
if(p->hasData(query)) return idx;
idx++;
}
throw 'cannot find the item';
}
void replace(int pos, int data){
if(this->empty() || !(pos>=0 && pos<size())) throw 'List is empty or out of range';
Node* node = getNode(pos);
node->setData(data);
}
int get(int pos){
if(this->empty() || !(pos>=0 && pos<size())) throw 'List is empty or out of range';
Node* node = getNode(pos);
return node->getData();
}
~SinglyLinkedList(){
while(!this->empty()) this->remove(0);
}
};Time complexity
- insert(pos, item) : O(n)
- remove(pos, item) : O(n)
- find(pos) : O(n)
- get/replace : O(n)
Space
- 2n : for n Node(data + link)
Pros & Cons
pros
- 가변 데이터 크기를 다룰 수 있다.
cons
- random access 불가
- 기본적인 연산 속도 느림
CircularLinkedList

Head를 없애고 Rear를 시작점으로 한다.
Rear에 시작하는 것이 갖는 장점
- addRear() : O(1)
- addFront() : O(1)
이전 단순 연결리스트에서는 맨뒤에 값을 넣기위해서는 n번의 탐색을 해야하는데, 맨 앞뒤에 삽입할때 시간복잡도가 O(1)으로 줄어든다.
Implementation
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node{
private:
int data;
Node* link;
public:
Node(int val=0) : data(val),link(nullptr){}
Node* get_link(){return this->link;}
void set_link(Node* next) {this->link = next;}
bool hasData(int val){return this->data == val;}
void setData(int data){this->data = data;}
int getData(){return this->data;}
};
class CircularSinglyLinkedList{
private:
Node rear;
int cnt;
Node* getRear(){return rear.get_link();}
Node* getNode(int pos){
Node* p = &rear;
// start at rear
pos = (pos + cnt) % cnt;
for(int i=-1; i<pos; i++){
if(p == nullptr) break;
p = p->get_link();
}
return p;
}
public:
CircularSinglyLinkedList(){
this->cnt = 0;
}
bool empty(){
return this->getRear() == nullptr;
}
int size() {return this->cnt;}
void display(){
cout<<"Size: "<<this->size()<<endl;
int i = 1;
for(Node* p = getRear()->get_link(); i<size(); p->get_link()){
cout<<p->getData()<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
void insert(int pos, int data){
if(!(pos>=0&&pos<=size())) throw 'out of range';
Node* prev = this->getNode(pos-1);
if(prev!=nullptr){
Node* p = new Node(data);
p->set_link(prev->get_link());
prev->set_link(p);
this->cnt++;
}
}
void remove(int pos){
if(!(pos>=0&&pos<=size())) throw 'out of range';
Node* prev = this->getNode(pos-1);
if(prev != nullptr){
Node* removed = prev->get_link();
prev->set_link(removed->get_link());
delete removed;
this->cnt--;
}
}
int find(int query){
int idx = 0;
for(Node* p = getRear()->get_link(); idx<size(); p->get_link()){
if(p->hasData(query)) return idx;
idx++;
}
throw 'cannot find the item';
}
void replace(int pos, int data){
if(this->empty() || !(pos>=0 && pos<size())) throw 'List is empty or out of range';
Node* node = getNode(pos);
node->setData(data);
}
int get(int pos){
if(this->empty() || !(pos>=0 && pos<size())) throw 'List is empty or out of range';
Node* node = getNode(pos);
return node->getData();
}
~CircularSinglyLinkedList(){
while(!this->empty()) this->remove(0);
}
};
DoublyLinkedList
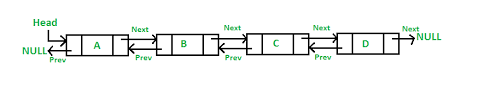
Implementation
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node{
private:
int data;
Node* prev;
Node* next;
public:
Node(int val=0) : data(val),prev(nullptr),next(nullptr){}
Node* get_prev(){return this->prev;}
Node* get_next(){return this->next;}
void set_next(Node* next){this->next = next;}
void set_prev(Node* prev){this->prev = prev;}
bool hasData(int val){return this->data == val;}
void setData(int data){this->data = data;}
int getData(){return this->data;}
};
class DoublyLinkedList{
private:
Node head;
int cnt;
Node* getHead(){return head.get_next();}
Node* getNode(int pos){
Node* p = &head;
for(int i=-1; i<pos; i++){
if(p == nullptr) break;
p = p->get_next();
}
return p;
}
public:
DoublyLinkedList(){
this->cnt = 0;
}
bool empty(){
return this->getHead() == nullptr;
}
int size(){return this->cnt;}
void display(){
cout<<"Size: "<<this->size()<<endl;
for(Node* p=getHead(); p!=nullptr; p=p->get_next()){
cout<<p->getData()<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
void insert(int pos, int data){
if(!(pos>=0&&pos<=size())) throw 'out of range';
Node* prev = this->getNode(pos-1);
Node* next = prev->get_next();
if(prev!=nullptr){
Node* p = new Node(data);
p->set_prev(prev);
p->set_next(next);
prev->set_next(p);
next->set_prev(p);
this->cnt++;
}
}
void remove(int pos){
if(!(pos>=0&&pos<=size())) throw 'out of range';
Node* removed = this->getNode(pos);
Node* prev = removed->get_prev();
Node* next = removed->get_next();
if(prev != nullptr){
prev->set_next(next);
next->set_prev(prev);
delete removed;
this->cnt--;
}
}
int find(int query){
int idx = 0;
for(Node* p=getHead(); p!=nullptr; p=p->get_next()){
if(p->hasData(query)) return idx;
idx++;
}
throw 'cannot find the item';
}
void replace(int pos, int data){
if(this->empty() || !(pos>=0 && pos<size())) throw 'List is empty or out of range';
Node* node = getNode(pos);
node->setData(data);
}
int get(int pos){
if(this->empty() || !(pos>=0 && pos<size())) throw 'List is empty or out of range';
Node* node = getNode(pos);
return node->getData();
}
~DoublyLinkedList(){
while(!this->empty()) this->remove(0);
}
};CircularDoublyLinkedList

Implementation
728x90
'Data Structrue' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Deque (덱) (0) | 2023.01.14 |
|---|---|
| Queue (큐) (0) | 2023.01.12 |
| Stack (스택) (0) | 2023.01.11 |
| What is Data Structure? (0) | 2023.01.11 |
Comments




